Comparison of Cold Pressing vs. Hot Stamping Technologies for Rock Drill Bits
Cold Pressing Technology
Principle: Achieves dimensional accuracy and bonding through mechanical pressure (500-1,500 MPa) at room temperature, utilizing high-precision molds and hydraulic presses to press tungsten carbide (WC) or other wear-resistant materials into pre-machined slots of the drill bit matrix.
Advantages:
1. Low Equipment Cost
• Requires standard hydraulic presses and molds, reducing capital expenditure.
2. Complex Geometry Compatibility
• Enables precise manufacturing of spiral grooves, chip evacuation holes, and non-circular profiles.
3. High Production Efficiency
• Short cycle time (15-30 minutes per piece) suitable for batch production and customized orders.
4. Energy Conservation
• Eliminates thermal energy consumption and CO₂ emissions.
5. Matrix Material Versatility
• Suitable for low-carbon steel, ductile iron, and other heat-sensitive matrices to prevent thermal distortion.

Disadvantages:
1. Limited Bonding Strength
• Mechanical interlocking provides bond strength of 200-500 MPa, prone to failure under high-impact/vibrational conditions.
2. Reduced Wear Resistance
• Localized stress concentration leads to rapid edge wear in abrasive environments.
3. Dimensional Stability Issues
• Mold wear may cause tolerances exceeding ±0.05 mm for critical features.
Application Scenarios:
• Soft to medium-hard rock drilling (limestone, sandstone) in shallow holes (<300 m depth);
• Applications requiring frequent bit replacement (e.g., small-scale mining operations);
• Budget-constrained projects with moderate performance requirements.
Hot Stamping Technology
Principle: Utilizes high-temperature processing (>800°C) to soften the matrix material, enabling metallurgical bonding with WC inserts through diffusion bonding or vacuum brazing.
Advantages:
1. Superior Bonding Strength
• Metallurgical integration achieves bond strength exceeding 1,000 MPa, suitable for deep-hole drilling under extreme loads.
2. High-Temperature Stability
• Operates reliably at temperatures up to 1,200°C with minimal oxidation of WC components.
3. Long Service Life
• Reduced wear rate by 300-500% compared to cold-pressed bits in hard-rock formations.
4. Vibration Resistance
• Homogeneous microstructure minimizes fatigue cracks under cyclic loading.
Disadvantages:
1. Complex Process Control
• Requires precise temperature regulation (±5°C tolerance) and atmosphere control (argon/nitrogen shielding).
2. High Production Costs
• Energy consumption for heating (15-20 kWh per batch) and specialized equipment depreciation.
3. Thermal Distortion Risks
• Matrix material expansion coefficient mismatch may cause angular deviation (>0.1°) during cooling.
4. Material Limitations
• Not suitable for high-carbon steels or titanium alloys due to intergranular脆化 during heating.
Application Scenarios:
• Deep-hole exploration (oil/gas, geothermal drilling) with depths exceeding 1,000 m;
• High-hardness rock drilling (granite, basalt) in mining and tunneling;
• Precision drilling tools for rotary-percussive machines requiring <5% bit wear rate.

Technical Comparison & Selection Guide
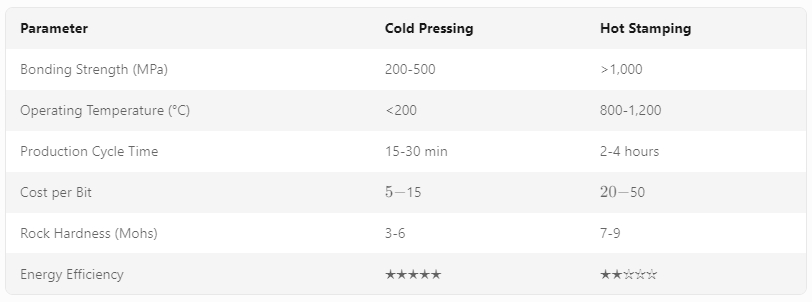
Selection Recommendations:
• Choose cold pressing for shallow-hole operations in soft rocks with budget constraints.
• Opt for hot stamping in deep-hole, high-hardness formations requiring drill bit lifetimes >200 hours.
Future Development Trends
1. Hybrid Manufacturing: Combining hot-stamping with post-pressing heat treatment to enhance bond strength while reducing thermal distortion.
2. Advanced Materials: Adoption of titanium-based matrices (Ti-6Al-4V) for hot-stamping to improve corrosion resistance and fatigue life.
3. Automation Integration: AI-driven process optimization for real-time parameter adjustment in hydraulic presses and vacuum furnaces.
4. Nanostructured Coatings: Deposition of diamond-like carbon (DLC) or titanium nitride (TiN) films on WC inserts to reduce abrasive wear by 40-60%.


